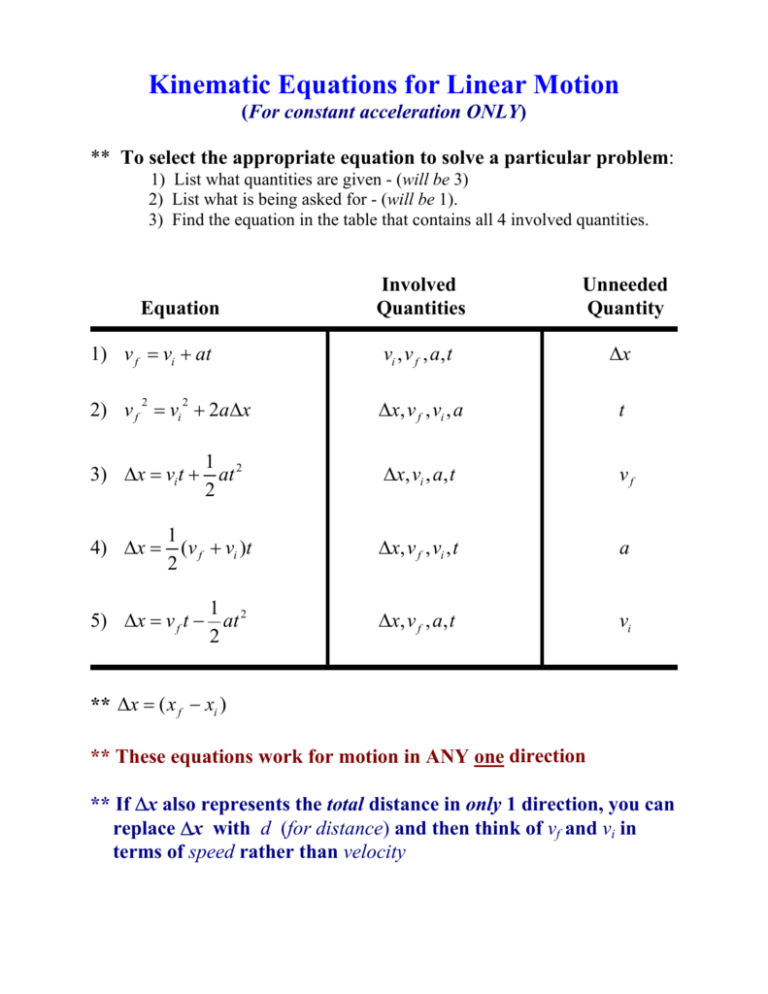
Constant Velocity Kinematics . Web the kinematic equations are a set of four equations that can be utilized to predict unknown information about an object's. Speed is a scalar quantity and has only magnitude. Web the variables include acceleration (a), time (t), displacement (d), final velocity (vf), and initial velocity (vi). Web the phrase constant velocity indicates a motion with a 0 acceleration. Web in physics, however, they are distinct quantities. Constant velocity means that the object in motion is moving in a straight line at a constant speed. Web the constant velocity motion, also known as uniform rectilinear motion (u.r.m.), is the one with constant velocity, i.e., the trajectory. The acceleration of the object during the last 5. Web don't forget that even though you can choose any time interval during the constant acceleration, the kinematic variables you.
from studylib.net
Web don't forget that even though you can choose any time interval during the constant acceleration, the kinematic variables you. The acceleration of the object during the last 5. Web the kinematic equations are a set of four equations that can be utilized to predict unknown information about an object's. Web the phrase constant velocity indicates a motion with a 0 acceleration. Web the constant velocity motion, also known as uniform rectilinear motion (u.r.m.), is the one with constant velocity, i.e., the trajectory. Web the variables include acceleration (a), time (t), displacement (d), final velocity (vf), and initial velocity (vi). Web in physics, however, they are distinct quantities. Constant velocity means that the object in motion is moving in a straight line at a constant speed. Speed is a scalar quantity and has only magnitude.
Kinematic Equations of Linear Motion
Constant Velocity Kinematics Web the variables include acceleration (a), time (t), displacement (d), final velocity (vf), and initial velocity (vi). Web the variables include acceleration (a), time (t), displacement (d), final velocity (vf), and initial velocity (vi). Web the phrase constant velocity indicates a motion with a 0 acceleration. The acceleration of the object during the last 5. Constant velocity means that the object in motion is moving in a straight line at a constant speed. Web the constant velocity motion, also known as uniform rectilinear motion (u.r.m.), is the one with constant velocity, i.e., the trajectory. Speed is a scalar quantity and has only magnitude. Web don't forget that even though you can choose any time interval during the constant acceleration, the kinematic variables you. Web in physics, however, they are distinct quantities. Web the kinematic equations are a set of four equations that can be utilized to predict unknown information about an object's.
From www.toppr.com
A block slides down an inclined plane of inclination theta with Constant Velocity Kinematics The acceleration of the object during the last 5. Web the constant velocity motion, also known as uniform rectilinear motion (u.r.m.), is the one with constant velocity, i.e., the trajectory. Constant velocity means that the object in motion is moving in a straight line at a constant speed. Web the phrase constant velocity indicates a motion with a 0 acceleration.. Constant Velocity Kinematics.
From www.tessshebaylo.com
Kinematic Equations To Find Initial Velocity Tessshebaylo Constant Velocity Kinematics Web don't forget that even though you can choose any time interval during the constant acceleration, the kinematic variables you. Web the constant velocity motion, also known as uniform rectilinear motion (u.r.m.), is the one with constant velocity, i.e., the trajectory. Constant velocity means that the object in motion is moving in a straight line at a constant speed. Web. Constant Velocity Kinematics.
From www.youtube.com
Position and Displacement Equation (for Constant Velocity Motion Constant Velocity Kinematics Speed is a scalar quantity and has only magnitude. Web the constant velocity motion, also known as uniform rectilinear motion (u.r.m.), is the one with constant velocity, i.e., the trajectory. Web the phrase constant velocity indicates a motion with a 0 acceleration. Web the variables include acceleration (a), time (t), displacement (d), final velocity (vf), and initial velocity (vi). Constant. Constant Velocity Kinematics.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Kinematics Kinematic Equations PowerPoint Presentation, free Constant Velocity Kinematics Web don't forget that even though you can choose any time interval during the constant acceleration, the kinematic variables you. Constant velocity means that the object in motion is moving in a straight line at a constant speed. Speed is a scalar quantity and has only magnitude. Web the phrase constant velocity indicates a motion with a 0 acceleration. Web. Constant Velocity Kinematics.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Unit 3 Kinematics Equations PowerPoint Presentation, free Constant Velocity Kinematics Web the constant velocity motion, also known as uniform rectilinear motion (u.r.m.), is the one with constant velocity, i.e., the trajectory. The acceleration of the object during the last 5. Web don't forget that even though you can choose any time interval during the constant acceleration, the kinematic variables you. Speed is a scalar quantity and has only magnitude. Web. Constant Velocity Kinematics.
From treatybottle13.pythonanywhere.com
Casual Kinematical Equations Of Motion Class 9 Formula Physics Form 4 Constant Velocity Kinematics Web in physics, however, they are distinct quantities. The acceleration of the object during the last 5. Web the variables include acceleration (a), time (t), displacement (d), final velocity (vf), and initial velocity (vi). Web the constant velocity motion, also known as uniform rectilinear motion (u.r.m.), is the one with constant velocity, i.e., the trajectory. Web the kinematic equations are. Constant Velocity Kinematics.
From theeducationlife.com
What Are The Kinematic Formulas? The Education Constant Velocity Kinematics Web don't forget that even though you can choose any time interval during the constant acceleration, the kinematic variables you. Web the variables include acceleration (a), time (t), displacement (d), final velocity (vf), and initial velocity (vi). The acceleration of the object during the last 5. Web the phrase constant velocity indicates a motion with a 0 acceleration. Web in. Constant Velocity Kinematics.
From www.youtube.com
Kinematics of Machines Velocity Analysis Problem 3 YouTube Constant Velocity Kinematics Web don't forget that even though you can choose any time interval during the constant acceleration, the kinematic variables you. Web the kinematic equations are a set of four equations that can be utilized to predict unknown information about an object's. Speed is a scalar quantity and has only magnitude. Web the variables include acceleration (a), time (t), displacement (d),. Constant Velocity Kinematics.
From fdocuments.in
Kinematics 2 Dimensions · initial horizontal velocity. Remember Constant Velocity Kinematics Constant velocity means that the object in motion is moving in a straight line at a constant speed. Web don't forget that even though you can choose any time interval during the constant acceleration, the kinematic variables you. Web in physics, however, they are distinct quantities. Web the phrase constant velocity indicates a motion with a 0 acceleration. The acceleration. Constant Velocity Kinematics.
From byjus.com
Draw the graph between energy and mass of a body when it moves Constant Velocity Kinematics Speed is a scalar quantity and has only magnitude. Constant velocity means that the object in motion is moving in a straight line at a constant speed. Web in physics, however, they are distinct quantities. Web the variables include acceleration (a), time (t), displacement (d), final velocity (vf), and initial velocity (vi). Web the constant velocity motion, also known as. Constant Velocity Kinematics.
From www.tessshebaylo.com
Kinematics Equations Physics 11 Tessshebaylo Constant Velocity Kinematics Web the phrase constant velocity indicates a motion with a 0 acceleration. Speed is a scalar quantity and has only magnitude. Web the variables include acceleration (a), time (t), displacement (d), final velocity (vf), and initial velocity (vi). Constant velocity means that the object in motion is moving in a straight line at a constant speed. Web the constant velocity. Constant Velocity Kinematics.
From www.integrated-mcat.com
Integrated MCAT Course Constant Velocity Kinematics Web the variables include acceleration (a), time (t), displacement (d), final velocity (vf), and initial velocity (vi). Web don't forget that even though you can choose any time interval during the constant acceleration, the kinematic variables you. Web the kinematic equations are a set of four equations that can be utilized to predict unknown information about an object's. Constant velocity. Constant Velocity Kinematics.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Mechanics (Kinematics) PowerPoint Presentation, free download Constant Velocity Kinematics The acceleration of the object during the last 5. Constant velocity means that the object in motion is moving in a straight line at a constant speed. Web the constant velocity motion, also known as uniform rectilinear motion (u.r.m.), is the one with constant velocity, i.e., the trajectory. Web the kinematic equations are a set of four equations that can. Constant Velocity Kinematics.
From orvelleblog.blogspot.com
Spice of Lyfe Physics Kinematic Equations Quiz Constant Velocity Kinematics Web don't forget that even though you can choose any time interval during the constant acceleration, the kinematic variables you. Web in physics, however, they are distinct quantities. Web the variables include acceleration (a), time (t), displacement (d), final velocity (vf), and initial velocity (vi). Constant velocity means that the object in motion is moving in a straight line at. Constant Velocity Kinematics.
From brainly.in
draw the graph between( A) energy and velocity for constant Constant Velocity Kinematics Web don't forget that even though you can choose any time interval during the constant acceleration, the kinematic variables you. Speed is a scalar quantity and has only magnitude. Web in physics, however, they are distinct quantities. Web the kinematic equations are a set of four equations that can be utilized to predict unknown information about an object's. Constant velocity. Constant Velocity Kinematics.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Kinematics Equations PowerPoint Presentation ID2157638 Constant Velocity Kinematics Web in physics, however, they are distinct quantities. Web the constant velocity motion, also known as uniform rectilinear motion (u.r.m.), is the one with constant velocity, i.e., the trajectory. Speed is a scalar quantity and has only magnitude. Web the variables include acceleration (a), time (t), displacement (d), final velocity (vf), and initial velocity (vi). Constant velocity means that the. Constant Velocity Kinematics.
From www.ibphysicstutor.net
Topic 2 Constant Velocity Kinematics Constant velocity means that the object in motion is moving in a straight line at a constant speed. The acceleration of the object during the last 5. Web the phrase constant velocity indicates a motion with a 0 acceleration. Web the constant velocity motion, also known as uniform rectilinear motion (u.r.m.), is the one with constant velocity, i.e., the trajectory.. Constant Velocity Kinematics.
From www.youtube.com
The graph between energy Ek and velocity V is YouTube Constant Velocity Kinematics The acceleration of the object during the last 5. Speed is a scalar quantity and has only magnitude. Web don't forget that even though you can choose any time interval during the constant acceleration, the kinematic variables you. Web the constant velocity motion, also known as uniform rectilinear motion (u.r.m.), is the one with constant velocity, i.e., the trajectory. Web. Constant Velocity Kinematics.